What is a transformer?
A transformer is an electrical machine with two or more windings. The magnetic induction between these windings makes it possible to adapt the electrical energy to the different voltage levels of the grids to which it is connected: grids for generation, long-distance transmission and low and intermediate voltage level distribution for the industrial or domestic sectors.
Consequently, transformers are an enormously important link in the chain for the entire electricity sector, with an estimated service lifetime of 30-40 years.
Why are power transformers monitored?
Although these are highly reliable assets (failure rate ~1%/year), there are multiple failure modes that might appear at any time, some of them catastrophic, such as short-circuiting between turns or winding hotspots. Transformers are subject to periodic inspections during scheduled outages (1-5 years) by means of in situ testing to determine their condition and degree of degradation. Nevertheless, failures may occur between outages and for this reason monitoring is applied.
How do we address monitoring?
Monitoring is based on the use of sensors located in the transformer, which pick up its status parameters when it is in service. At Tecnatom we install the EMS TCM (Transformer Condition Monitor) system, based on the collection of electrical variables used as sensors by the measuring transformers available at the plant. Consequently, electrical variables are diagnosed, the most relevant being the magnetising current. Advanced algorithms are used to obtain a severity factor of sufficient sensitivity to promptly detect problems, determining their origin: windings, magnetic plate or tap changer.
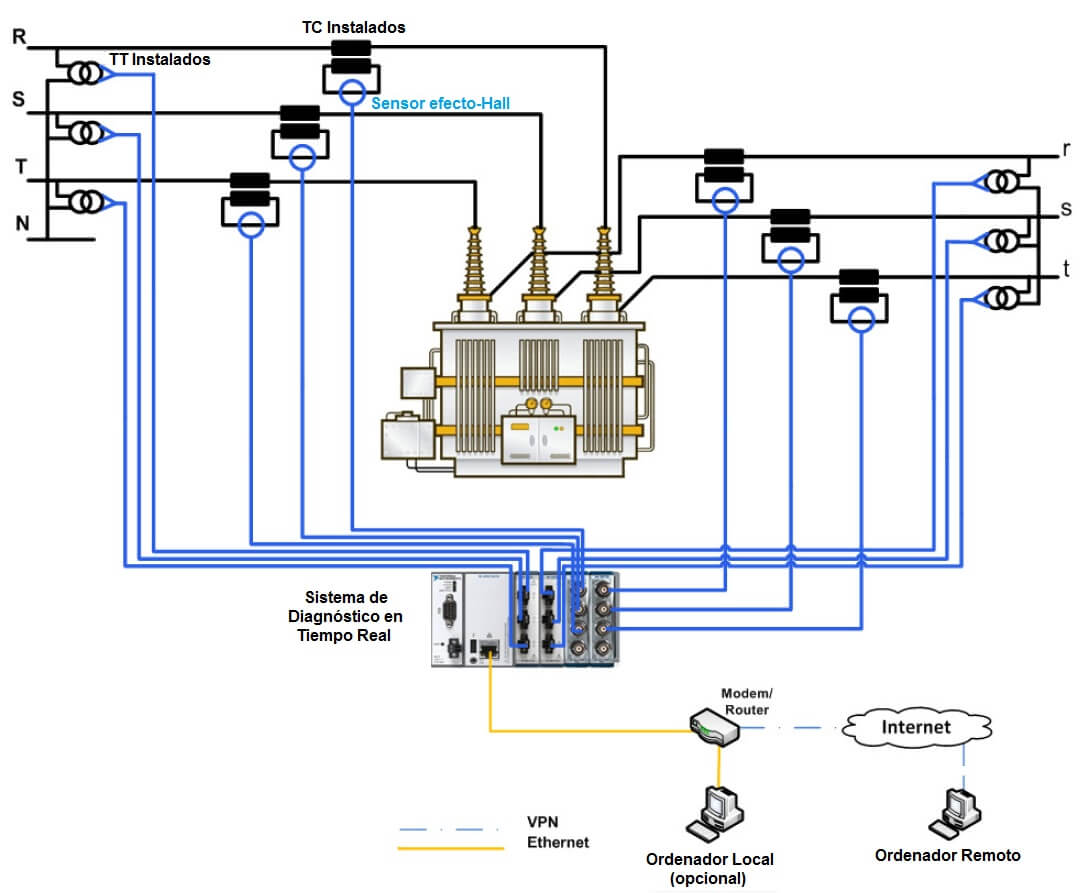
What do we do at Tecnatom?
We provide continuous support for different Spanish nuclear power plants, where we undertake the monitoring of several of their transformers. At present we are concluding the pilot phases for a number of systems that monitor transformers of more than 300MW. In addition we are also developing solutions for the renewable energy sector, with technological proposals allowing for the monitoring of wind turbines, covering both the transformer and the generator itself, the multiplier and the control electronics.
Author: Andrés Tabernero